In this tutorial, we’ll cover how to move, copy, and rename directories within Linux, using the terminal and some easy commands.
Use the table of contents below to find a specific section or read on to learn more!
How to Move a Directory in Linux
If you’re trying to move a directory in Linux from one location to another, just follow these 4 steps:
- If you want to move a directory or file in Linux, you can use the move command, followed by the Source (the directory you’re moving) and Destination (the directory you’re moving it to):
mv [Source] [Destination]
- So, if you wanted to move /directory1 into a second directory name /directory2, you would use the following command:
mv /directory1 /directory2

*Note: If no “/directory2” exists, /directory1 will be renamed as “/directory2”, essentially “moving” it into a newly created directory.
- This can also be done for multiple files and directories at once. Let’s say you have 3 files (file1, file2, and file3), and you’d like to move all them into /directory1. Simply list out all your sources before your destination, and Linux will automatically move all these files at once.
mv file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt /home/directory1
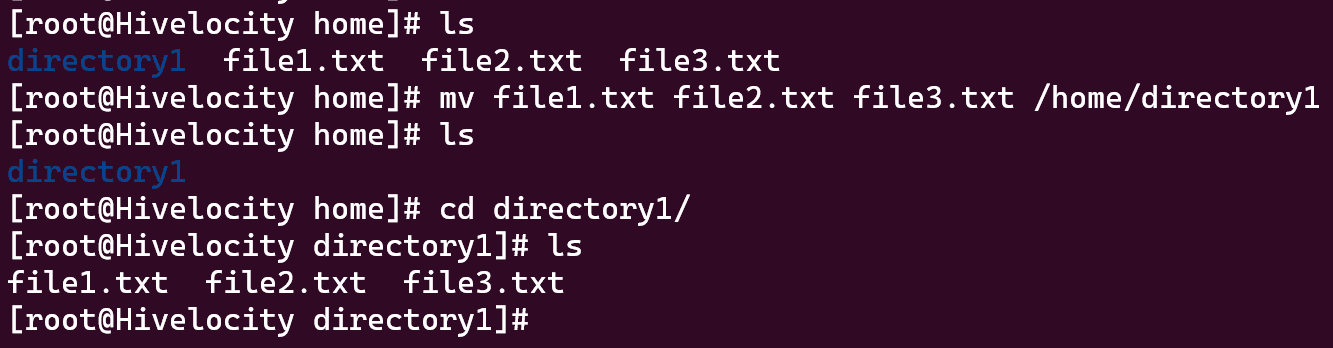
- Keep in mind that in order to move files and directories, a user must have permissions allowing them to modify both the source and destination directories. Otherwise, an error will occur and permission will be denied.
How to Copy a Directory in Linux
If you’re trying to make a copy of an existing directory, just follow these 4 steps:
- To copy a directory or file in linux, just use the copy command followed by the Source (the directory you’re copying), and the Destination (the place you’re copying it to):
cp -R [Source] [Destination]
- So, if you wanted to make a copy of /directory1 and place it inside of /directory2, you would use the command:
cp -R /directory1 /directory2

*Note: If no “/directory2” exists, a new directory will be created, with that name, and containing the contents of /directory1.
- Like moving files, it is possible to copy multiple files into a single directory by listing out multiple filenames for sources, followed by a single destination. For example:
cp -R file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt /directory1

Which, as shown above, copies file1, file2, and file3, placing their copies in /directory1.
- Additionally, if you wanted to copy the entire contents of /directory1 into /directory2 (duplicating the files inside the folder but not the folder itself), you can do so by adding ” /* ” after the source directory. For example:
cp – R /directory1/* /directory2

As shown above, this creates copies of all the files located in /directory1, placing duplicates of its content into /directory2, but not duplicating the actual directory itself.
How to Rename a Directory in Linux
If you need to rename an existing directory in Linux to something new, just follow these 2 steps:
- Interestingly, due to the way Linux’s file structures work, moving a file and renaming a file are actually the same action. This is because when you’re “moving” a file in Linux, you’re really “renaming” its file path: giving it a new name but also a new location in your system’s structure.
mv [Source] [NewName]
- So, to rename /directory1 to /directory_new, you would use the command:
mv /directory1 /directory_new

*Note: If “/directory_new” already exists, then this command will move the contents of /directory1 to /directory_new. However, if “/directory_new” does NOT already exist, this command will rename /directory1 to /directory_new.
Popular Links
Looking for more information on Linux? Search our Knowledge Base!
Interested in more articles about Operating Systems? Navigate to our Categories page using the bar on the left or check out these popular articles:
- How to Check the Apache Version on a Linux Dedicated cPanel Server
- How to Change a Password in Linux
- How to Check if Your Linux Server is Under DDoS Attack
Popular tags within this category include: Linux, Windows, Apache, CentOS, Debian, Fedora, RedHat, and more.
Don’t see what you’re looking for? Use the search bar at the top to search our entire Knowledge Base.
The Hivelocity Difference
Seeking a better Dedicated Server solution? In the market for Private Cloud or Colocation services? Check out Hivelocity’s extensive list of products for great deals and offers.
With best-in-class customer service, affordable pricing, a wide-range of fully-customizable options, and a network like no other, Hivelocity is the hosting solution you’ve been waiting for.
Unsure which of our services is best for your particular needs? Call or live chat with one of our sales agents today and see the difference Hivelocity can make for you.