Starting, stopping, and restarting the MySQL server are fundamental administrative tasks that administrators must perform regularly. These actions are necessary when conducting maintenance, troubleshooting issues, or implementing configuration changes. Understanding these operations is critical for maintaining the overall health and performance of the database. In this guide, we will walk you through the essential commands for managing the MySQL service safely across both Linux and Windows operating systems. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your database remains consistently available and reliable.
Managing the MySQL Service in Linux
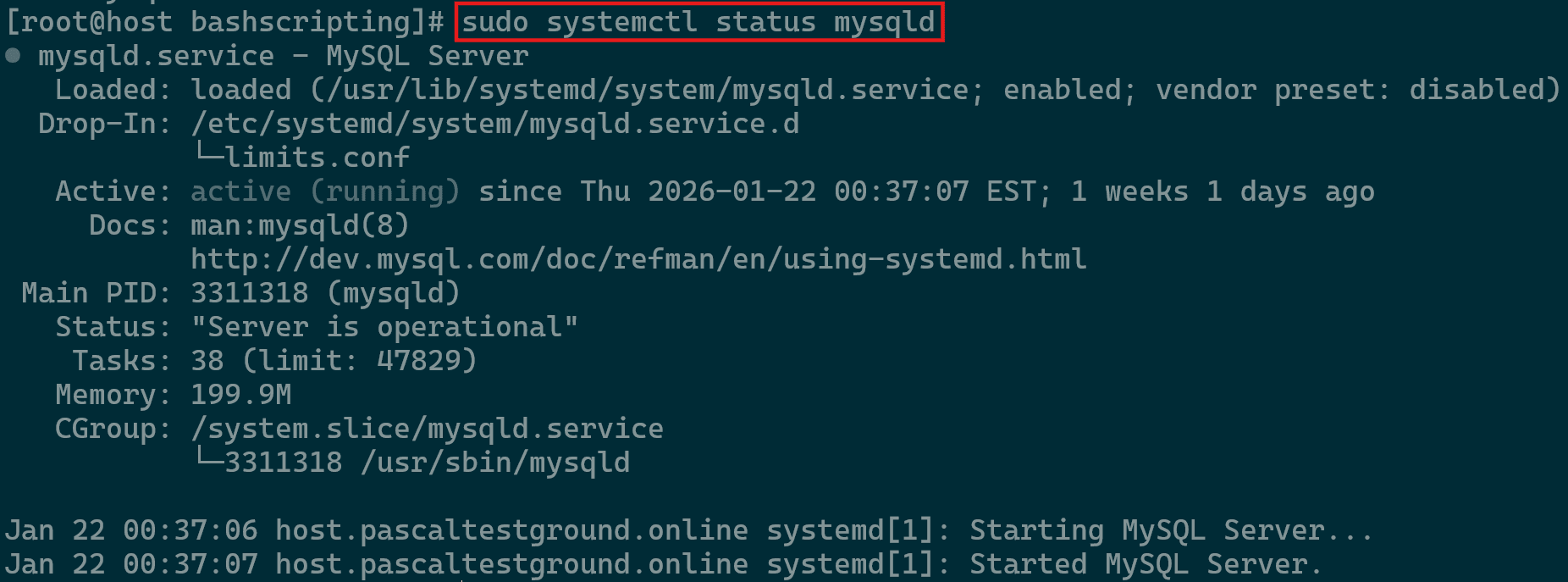
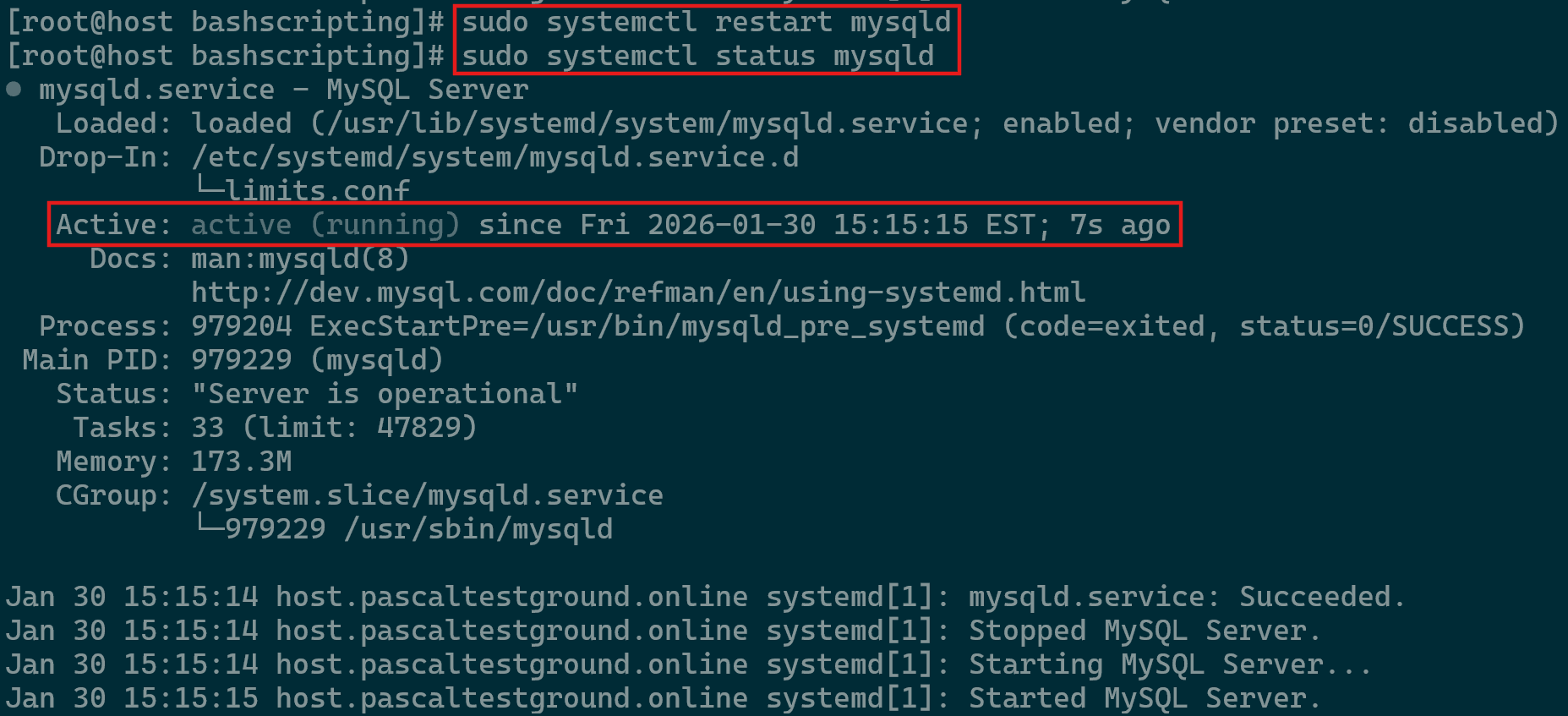
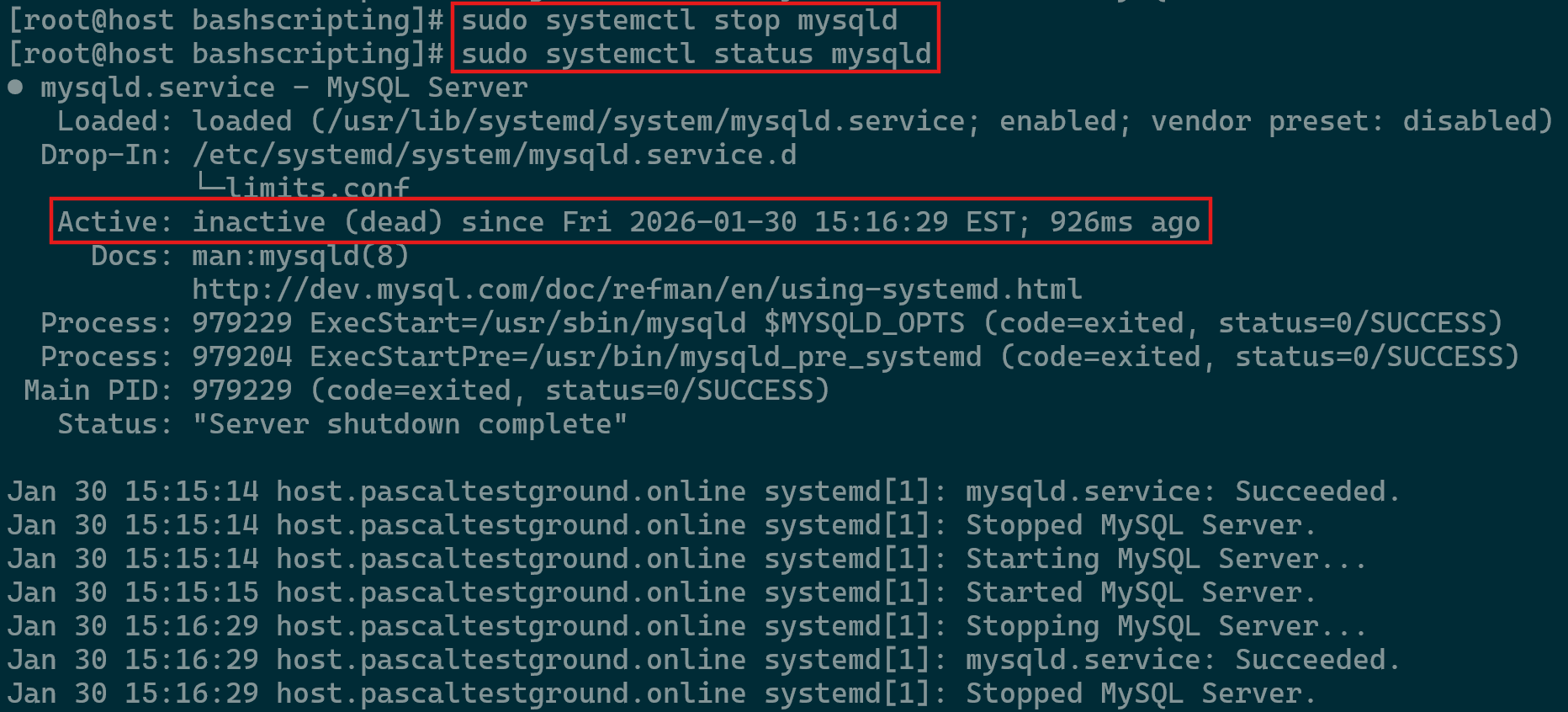
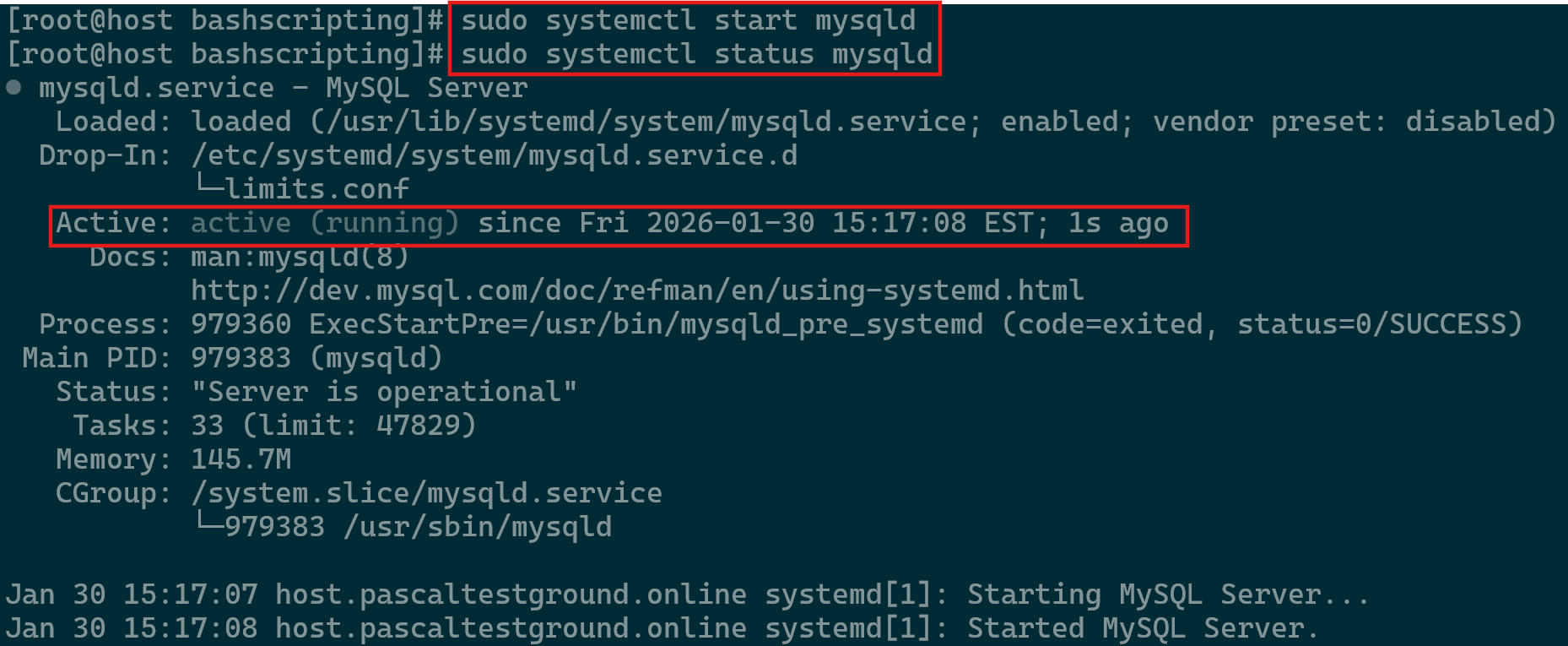
Managing the MySQL service in Linux is a routine responsibility for both developers and system administrators. Whether you’re implementing configuration updates or resolving service issues, understanding how to control the service is essential. Proper management helps ensure the database remains stable and responsive during various operational conditions. This section introduces the primary methods used on Linux systems to maintain a reliable MySQL environment.
Managing the MySQL Service in Windows
Similarly to Linux, managing the MySQL service in Windows is a critical administrative task. In many scenarios, such as routine maintenance or troubleshooting, it is essential to have a thorough understanding of service controls. As a result, by mastering how to manage the service efficiently, you not only simplify administration but also enhance overall system reliability.
Do not confuse MySQL with Microsoft SQL Server (MSSQL). These platforms are distinct despite their shared nomenclature. Consequently, you must utilize specialized tools tailored specifically to each environment. Since the underlying architectures differ, commands used in one system will not work in the other.
Important Tips
- Always run CMD (Command Prompt) as Administrator to avoid “Access Denied” errors.
- Confirm the name in
services.mscfirst, otherwise your commands will likely fail. - Locate
my.iniin the hiddenC:\ProgramDatafolder and ensure “Hidden Items” is enabled. - Use the
stopcommand instead of Task Manager to prevent data corruption (Avoid Task Manager to kill this service if you can). - Set the service to Automatic, as a result the database remains active after every reboot.
Managing with Command Prompt
In many situations, Windows service names are versioned (for example, MySQL80). Because of this, it is recommended that you first confirm the exact service name. By doing so, you ensure that your commands execute as intended. This reduces the likelihood of errors and prevents unnecessary troubleshooting.
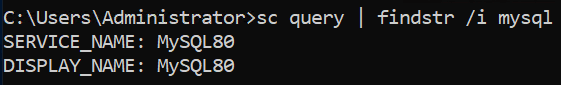
List All MySQL Services
Use this to find the exact name of your MySQL service (e.g., MySQL80 or mysql).
Command: sc query | findstr /i mysql
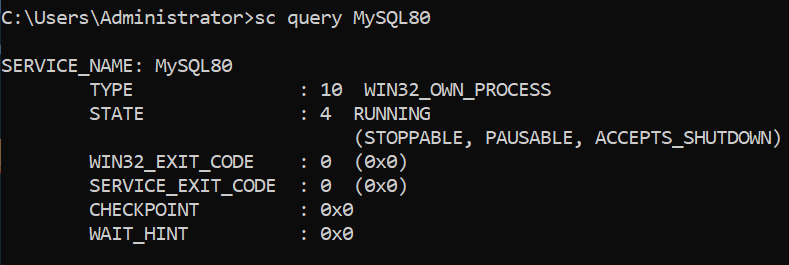
Check Specific Service Status
Verify if the MySQL service is “RUNNING” or “STOPPED”. Replace MySQL with your specific service name if it differs.
Command: sc query MySQL
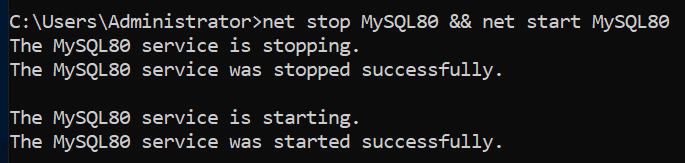
Restart MySQL
Windows doesn’t have a single “restart” command in CMD, so you chain the stop and start commands together.
Command: net stop MySQL && net start MySQL
Stop MySQL Service
Command: net stop MySQLor sc stop MySQL
Start MySQL Service
Command: net start MySQL or sc start MySQL
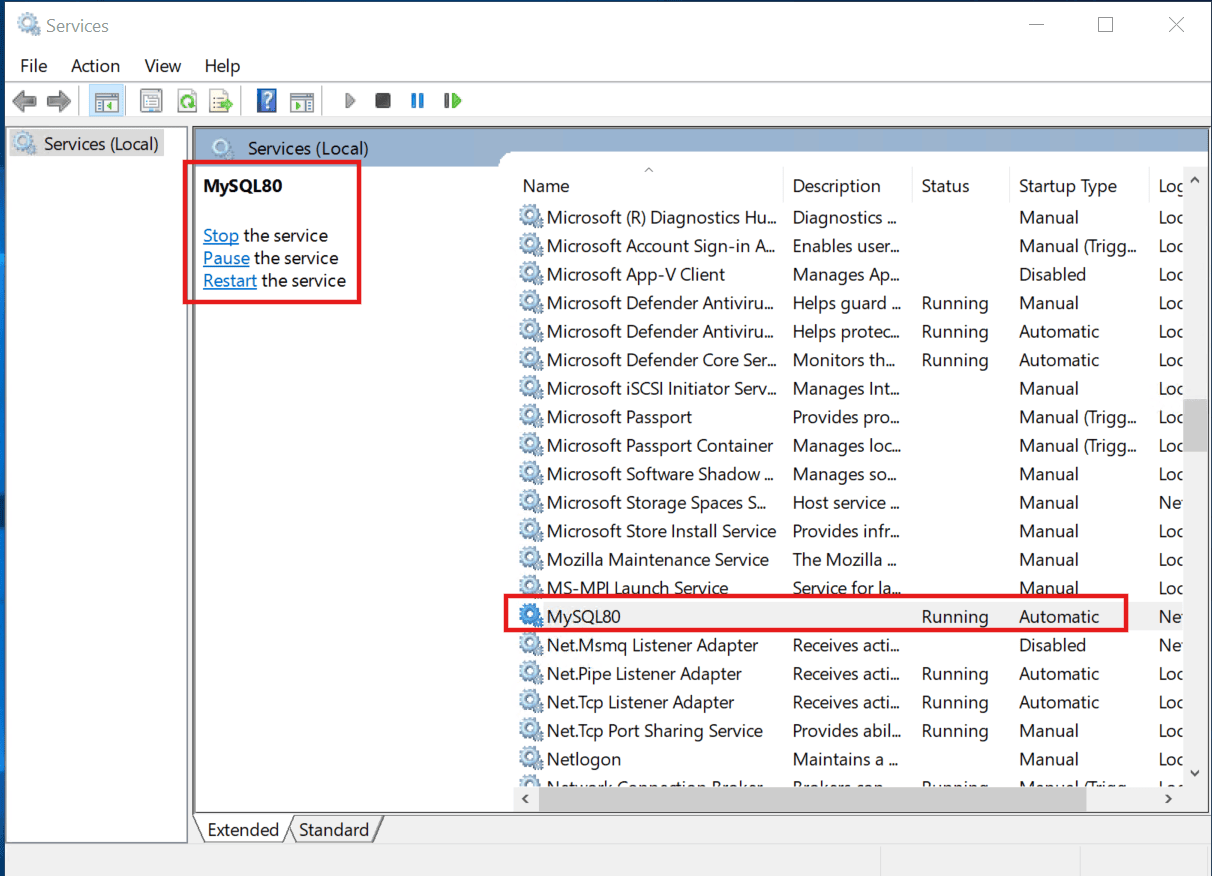
Managing with Services.msc (Graphical Interface)
To open the Services utility, start by pressing Windows Key + R, typing services.msc, and hitting Enter. Once the window appears, you can locate the MySQL entry to apply a stop, pause, or restart as necessary.
— Written by Pascal Suissa