AWS Egress Fees Explained: What You’re Really Paying to Leave
Moving data out of Amazon Web Services isn’t just a technical consideration—it’s a financial one that can significantly impact your cloud budget. AWS egress fees, the charges applied when data leaves Amazon’s network, have become one of the most scrutinized aspects of cloud economics. These costs can accumulate rapidly for data-intensive applications, often catching organizations off guard when monthly bills arrive.
Understanding AWS egress pricing structure becomes crucial as businesses evaluate cloud strategies, consider multi-cloud architectures, or plan potential migrations. Recent regulatory changes, particularly the EU Data Act, have prompted AWS to adjust its egress policies, creating new opportunities for cost optimization and migration planning.
This comprehensive analysis examines AWS egress fees, their pricing structure, recent policy changes, and practical strategies for cost optimization. We’ll also explore how these fees factor into broader cloud architecture decisions and migration considerations.
What Are AWS Egress Fees?
AWS egress fees, also known as Data Transfer Out (DTO) charges, represent costs incurred when data leaves the AWS network. These charges apply to various scenarios: data downloaded from EC2 instances to the internet, S3 object retrievals by external users, cross-region data synchronization, and traffic between different Availability Zones (AZs).
The fundamental principle underlying egress fees is straightforward—AWS charges for outbound data movement while keeping inbound data transfer (ingress) free. This asymmetric pricing model reflects the infrastructure costs associated with delivering data to external destinations and maintaining global network capacity.
Common triggers for egress charges include:
- Web traffic served directly from EC2 instances or S3 buckets
- Database replication across regions
- Backup data transferred to external storage systems
- API responses delivered to client applications
- Content delivery without proper CDN optimization
Why AWS Charges Egress Fees
AWS justifies egress fees based on infrastructure investment and operational costs. The company maintains a global network spanning multiple continents, requiring significant capital expenditure for bandwidth provisioning, peering agreements with internet service providers, and edge location maintenance.
From AWS’s perspective, egress fees also serve as a business strategy tool. By making data movement costly, AWS incentivizes customers to keep workloads within their ecosystem, reducing migration likelihood and increasing customer lifetime value. This approach, common among major cloud providers, has drawn regulatory attention in recent years.
The pricing model encourages architectural decisions that favor AWS services. Organizations naturally gravitate toward keeping databases, compute resources, and applications within the same AWS region to minimize cross-region transfer costs, creating stronger ecosystem lock-in.
AWS Egress Fees Structure and Pricing
AWS employs a tiered pricing model for internet egress, where per-gigabyte costs decrease as total monthly data transfer volumes increase. The current structure includes a 100 GB free tier (increased from 1 GB in 2024) aggregated across all AWS services and regions, excluding China and GovCloud.
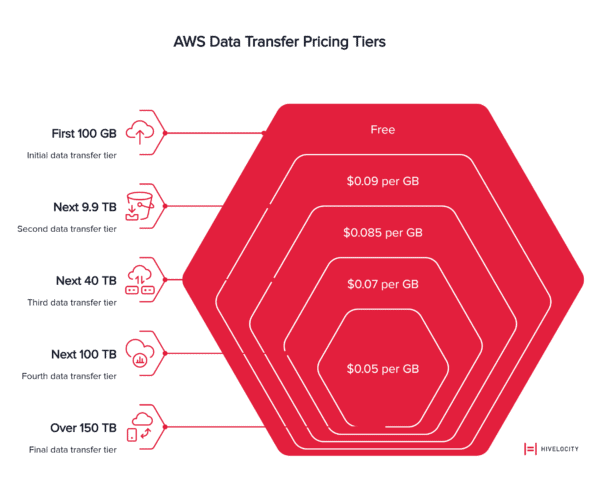
Internet Egress Pricing (US East – N. Virginia):
- First 100 GB per month: Free
- Next 9.9 TB per month: $0.09 per GB
- Next 40 TB per month: $0.085 per GB
- Next 100 TB per month: $0.07 per GB
- Over 150 TB per month: $0.05 per GB
Cross-Region Data Transfer typically costs $0.02 per GB for most common region pairs, such as traffic between US and European regions. However, adjacent regions offer lower rates—for instance, data transfer between US East (N. Virginia) and US East (Ohio) costs $0.01 per GB.
Cross-Availability Zone transfers incur $0.01 per GB charges in each direction, while data transfer within the same AZ using private IP addresses remains free. This pricing structure significantly influences architectural decisions, encouraging resource co-location within single availability zones when possible.
CloudFront CDN pricing varies by geographic region, with US and Europe rates starting at $0.085 per GB for the first 10 TB monthly, while Asia-Pacific regions may charge $0.14 per GB or higher.
Strategies to Minimize AWS Egress Costs
Effective egress cost management requires combining architectural optimization, service selection, and operational best practices. Organizations can implement multiple strategies simultaneously for maximum impact.
Learn more: Taming the AWS Bill: How to Regain Control of Your Cloud Costs
Leverage the 100GB Free Tier
AWS provides 100 GB of monthly internet egress free across all services and regions. Smaller applications and development environments can often operate entirely within this allowance, eliminating egress charges completely.
Optimize Data Transfer Locations
Keeping resources within the same Availability Zone eliminates cross-AZ transfer charges. While this approach may reduce fault tolerance, cost-conscious organizations can balance availability requirements against transfer costs through careful architectural planning.
Implement CloudFront CDN
AWS CloudFront offers 1 TB of free egress monthly, significantly exceeding the base 100 GB allowance. By caching frequently accessed content at edge locations, organizations can reduce origin server egress while improving global performance. CloudFront’s geographic distribution also provides more favorable pricing for international traffic.
Deploy Data Compression
Implementing compression algorithms like Gzip or Brotli for text-based content (HTML, CSS, JSON, API responses) can reduce data transfer volumes by 60-80%. Modern compression techniques work particularly well for repetitive data structures common in web applications and API communications.
Consider Multi-Cloud Architecture
Organizations with substantial data transfer requirements should evaluate multi-cloud or hybrid strategies. While complexity increases, distributing workloads across providers can reduce dependence on any single vendor’s egress pricing. This approach works particularly well for organizations with significant on-premises infrastructure or specific geographic requirements.
Utilize Migration Credits
AWS now offers 60-90 days of free data transfer credits for approved migrations off the platform. Organizations planning migrations should coordinate with AWS support to maximize these credits, potentially saving thousands of dollars during transition periods.
Recent Changes in AWS Egress Policy
The European Union’s Data Act has prompted significant changes in AWS egress policies, reflecting broader regulatory pressure for improved cloud data portability. These modifications demonstrate how regulatory frameworks can influence cloud provider pricing strategies.
Increased Free Allowance
AWS expanded the free monthly egress allowance from 1 GB to 100 GB per account in 2024, representing a 10,000% increase. This change benefits smaller organizations and development workloads significantly, potentially eliminating egress charges for many use cases.
Migration Credit Program
AWS introduced a formal migration credit program providing 60-90 days of free data transfer for customers leaving the platform. This program directly addresses EU Data Act requirements for data portability, removing cost barriers for organizations seeking provider alternatives.
Explicit Regulatory Compliance
AWS’s public acknowledgment of the EU Data Act’s influence on these policy changes signals recognition of regulatory oversight in cloud economics. This transparency suggests continued policy evolution as international data governance frameworks mature.
These changes create opportunities for organizations to reassess cloud strategies and negotiate better terms with AWS or evaluate alternative providers.
Alternative Cloud Solutions: Hivelocity Enterprise Cloud
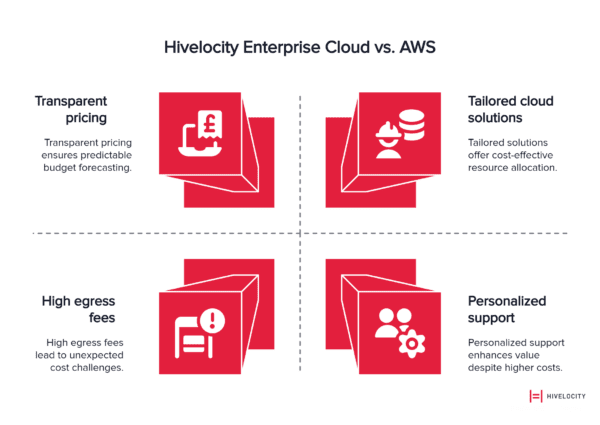
While AWS egress fees present ongoing cost challenges, alternative cloud providers offer different economic models that may better align with specific organizational requirements. Hivelocity Enterprise Cloud exemplifies this alternative approach through transparent pricing and predictable cost structures.
Transparent Pricing Models
Hivelocity eliminates hidden egress fees common in hyperscale cloud platforms, providing straightforward pricing that enables accurate budget forecasting. Organizations can predict monthly costs without complex egress calculations or surprise charges from unexpected data transfer patterns.
Competitive Data Transfer Rates
Hivelocity’s data transfer pricing significantly undercuts AWS egress fees, particularly beneficial for data-intensive applications, content delivery, backup operations, and real-time analytics platforms. These savings compound monthly, creating substantial annual cost reductions.
Customized Solutions and Expert Support
Unlike AWS’s standardized service offerings, Hivelocity provides tailored cloud solutions with personalized support throughout deployment and operation. This approach ensures optimal resource allocation and cost efficiency for specific organizational requirements.
Strategic Geographic Positioning
Hivelocity operates data centers in key locations, enabling organizations to optimize data residency for regulatory compliance while maintaining low-latency access to end users. This geographic strategy reduces the need for expensive cross-region data transfers.
Simplified Migration Process
Hivelocity offers comprehensive migration services to ease transitions from AWS, minimizing disruption while ensuring seamless onboarding. Expert migration support reduces technical risks and accelerates time-to-value for new cloud deployments.
Managing AWS Egress Fees Effectively
AWS egress fees represent a significant component of cloud economics that requires proactive management and strategic planning. Understanding the pricing structure, leveraging optimization strategies, and staying informed about policy changes enables organizations to control these costs effectively.
The recent increases in free allowances and introduction of migration credits demonstrate how regulatory pressure can influence cloud provider policies. Organizations should monitor these developments and reassess their cloud strategies accordingly.
For organizations seeking alternatives to AWS’s complex egress pricing, providers like Hivelocity offer transparent, cost-effective solutions without compromising performance or reliability. The decision to migrate or adopt multi-cloud strategies should factor in both immediate cost savings and long-term operational benefits.
Successful egress cost management ultimately requires balancing technical requirements, financial constraints, and strategic objectives. Organizations that proactively address these considerations will achieve better cost predictability and operational efficiency in their cloud deployments.
Ready to explore transparent cloud pricing without hidden egress fees? Learn more about Hivelocity Enterprise Cloud and discover how predictable pricing can transform your cloud cost management strategy.


